Testing Markov Chain Monte Carlo sampling algorithm¶
@Author: Ettore Biondi - ebiondi@caltech.edu
Problem definition¶
Now, we turn our attention onto sampling methods. We start with the very well-known sampling method called MCMC. We are going to extract samples of the following probability density function (PDF):
where two Gaussian multivariate distributions have been normalized summed together.
import numpy as np
import occamypy as o
o.backend.set_seed_everywhere(42)
# Plotting
from matplotlib import rcParams
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import make_axes_locatable
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
rcParams.update({
'image.cmap' : 'jet',
'image.aspect' : 'auto',
'image.interpolation': None,
'axes.grid' : False,
'figure.figsize' : (10, 6),
'savefig.dpi' : 300,
'axes.labelsize' : 14,
'axes.titlesize' : 16,
'font.size' : 14,
'legend.fontsize': 14,
'xtick.labelsize': 14,
'ytick.labelsize': 14,
'text.usetex' : True,
'font.family' : 'serif',
'font.serif' : 'Latin Modern Roman',
})WARNING! DATAPATH not found. The folder /tmp will be used to write binary files
/nas/home/fpicetti/miniconda3/envs/occd/lib/python3.10/site-packages/dask_jobqueue/core.py:20: FutureWarning: tmpfile is deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use dask.utils.tmpfile instead.
from distributed.utils import tmpfile
We first start by writing the problem class definition.
class TwoGaussians(o.Problem):
"""
Two Gaussian modes in a 2D plane
"""
def __init__(self, mu1, mu2, sigma1, sigma2):
"""
TwoGaussians constructor
Args:
mu1: 1D array - mean of the gaussian function 1
mu2: 1D array - mean of the gaussian function 2
sigma1: 2D array - variance matrix of gaussian function 1
sigma2: 2D array - variance matrix of gaussian function 2
"""
super(TwoGaussians, self).__init__(model=o.VectorNumpy(mu1.shape), data=o.VectorNumpy((1,)))
# Gaussian parameters
self.mu1 = mu1
self.mu2 = mu2
self.sigma1_inv = np.linalg.inv(sigma1)
self.sigma2_inv = np.linalg.inv(sigma2)
self.scale1 = 0.5 / (np.sqrt(np.linalg.det(sigma1) * (2.0 * np.pi) ** self.mu1.shape[0]))
self.scale2 = 0.5 / (np.sqrt(np.linalg.det(sigma2) * (2.0 * np.pi) ** self.mu2.shape[0]))
# Gradient vector
self.grad = self.pert_model.clone()
self.setDefaults()
self.linear = False
def res_func(self, model):
"""Residual function"""
m1 = model[:] - self.mu1
m2 = model[:] - self.mu2
self.res[0] = self.scale1 * np.exp(-0.5 * np.dot(m1, np.dot(self.sigma1_inv, m1))) + \
self.scale2 * np.exp(-0.5 * np.dot(m2, np.dot(self.sigma2_inv, m2)))
return self.res
def obj_func(self, residual):
"""Objective function computation"""
obj = residual[0]
return objBuild the PDF¶
mu1 = np.array([2.0, 1.5])
mu2 = np.array([-1.5, -3.0])
sigma1 = np.array([[1., 3. / 5.], [3. / 5., 2.]])
sigma2 = np.array([[2., -3. / 5.], [-3. / 5., 1.]])
problem = TwoGaussians(mu1, mu2, sigma1, sigma2)Let's now perform an extensive search, which will help us understand how the sampling method is performing on this PDF.
#Computing the objective function for plotting
xaxis = np.linspace(-5.,5.,100)
yaxis = np.linspace(-6.,6.,110)
pdf = o.VectorNumpy((yaxis.size, xaxis.size))
sample = o.VectorNumpy((2,))
for iy, y in enumerate(yaxis):
for ix, x in enumerate(xaxis):
sample[:] = y, x
pdf[iy,ix] = problem.get_obj(sample)fig, ax = plt.subplots()
im = plt.imshow(np.flip(pdf.plot(), axis=0), clim=(0,.07), extent=[-5.,5.,-6.,6.0])
ax.set_xlabel("x"), ax.set_ylabel("y")
cs = plt.contour(xaxis, yaxis, pdf.plot(),
levels=[0.01,0.02,0.03,0.04,0.05,0.06],
colors="black", linewidths=(0.8,), linestyles='--')
plt.colorbar(im, cax=make_axes_locatable(ax).append_axes("right", size="2%", pad=0.1))
plt.suptitle(r"$\phi(x,y)$")
plt.show()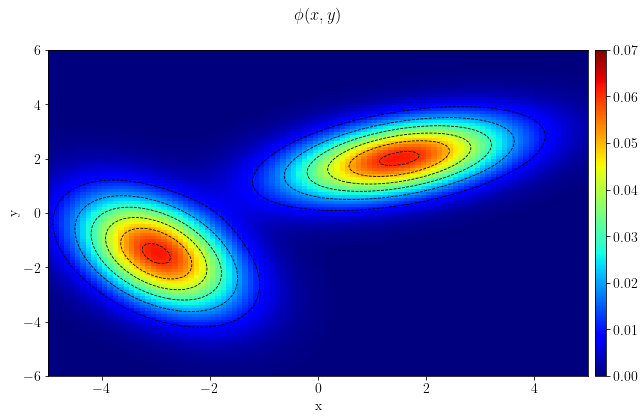
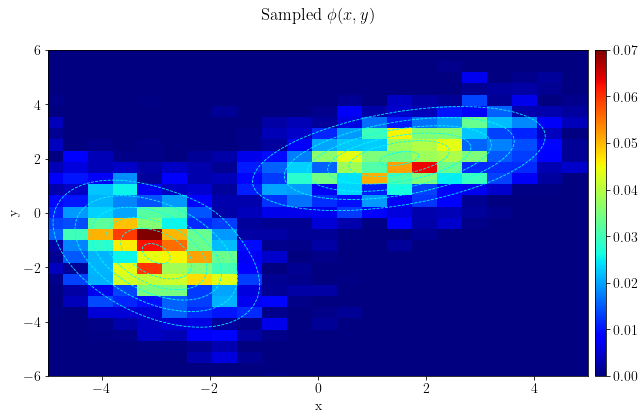
Sample the PDF with a MCMC method¶
MCMCsampler = o.MCMC(stopper=o.SamplingStopper(10000), prop_distr="u", max_step=2.5)
MCMCsampler.setDefaults()
MCMCsampler.run(problem, verbose=False)# Converting sampled points to arrays for plotting
burn_samples = 500
MCMC_samples = np.array([MCMCsampler.model[i].getNdArray()
for i in range(burn_samples, len(MCMCsampler.model))], copy=False)fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.hist2d(MCMC_samples[:,1], MCMC_samples[:,0], bins=[30,30])
ax.set_xlabel("x"), ax.set_ylabel("y")
ax.set_xlim(-5,5), ax.set_ylim(-6,6)
cs = plt.contour(xaxis, yaxis, pdf.plot(),
levels=[0.01,0.02,0.03,0.04,0.05,0.06],
colors="cyan", linewidths=(0.8,), linestyles='--')
plt.colorbar(im, cax=make_axes_locatable(ax).append_axes("right", size="2%", pad=0.1))
plt.suptitle(r"Sampled $\phi(x,y)$")
plt.show()